Dental Health Sensing Using a Sonic Toothbrush
Early detection of dental disease is crucial to prevent adverse outcomes. Today, dental X-rays are currently the most accurate gold standard for dental disease detection. Unfortunately, regular X-ray exam is still a privilege for billions of people around the world. In this paper, we ask: "Can we develop a low-cost sensing system that enables dental self-examination in the comfort of one’s home?" This project presents ToMoBrush, a dental health sensing system that explores using off-the-shelf sonic toothbrushes for dental condition detection. Our solution leverages the fact that a sonic toothbrush produces rich acoustic signals when in contact with teeth, which contain important information about each tooth’s status. ToMoBrush extracts tooth resonance signatures from the acoustic signals to characterize the dental condition of each tooth.

Battery-free Wideband Spectrum Mapping
In this project, we introduce RFIMap, a system that aims to inexpensively characterize the spatial and temporal distribution of RF spectrum occupancy of any indoor space at fine granularity (tens of centimeters). RFIMap builds rich wide-band indoor spectrum occupancy maps using low-cost and batteryfree commodity RFID tags. RFIMap’s spectrum maps have wide-ranging applications such as monitoring ambient interference in smart manufacturing, and smart hospitals. . RFIMap relies on the observation that commodity RFID tags naturally refect ambient transmission at other frequency bands, without any modifcation. RFIMap uses these refections to estimate the ambient signal power originally received at these tags.
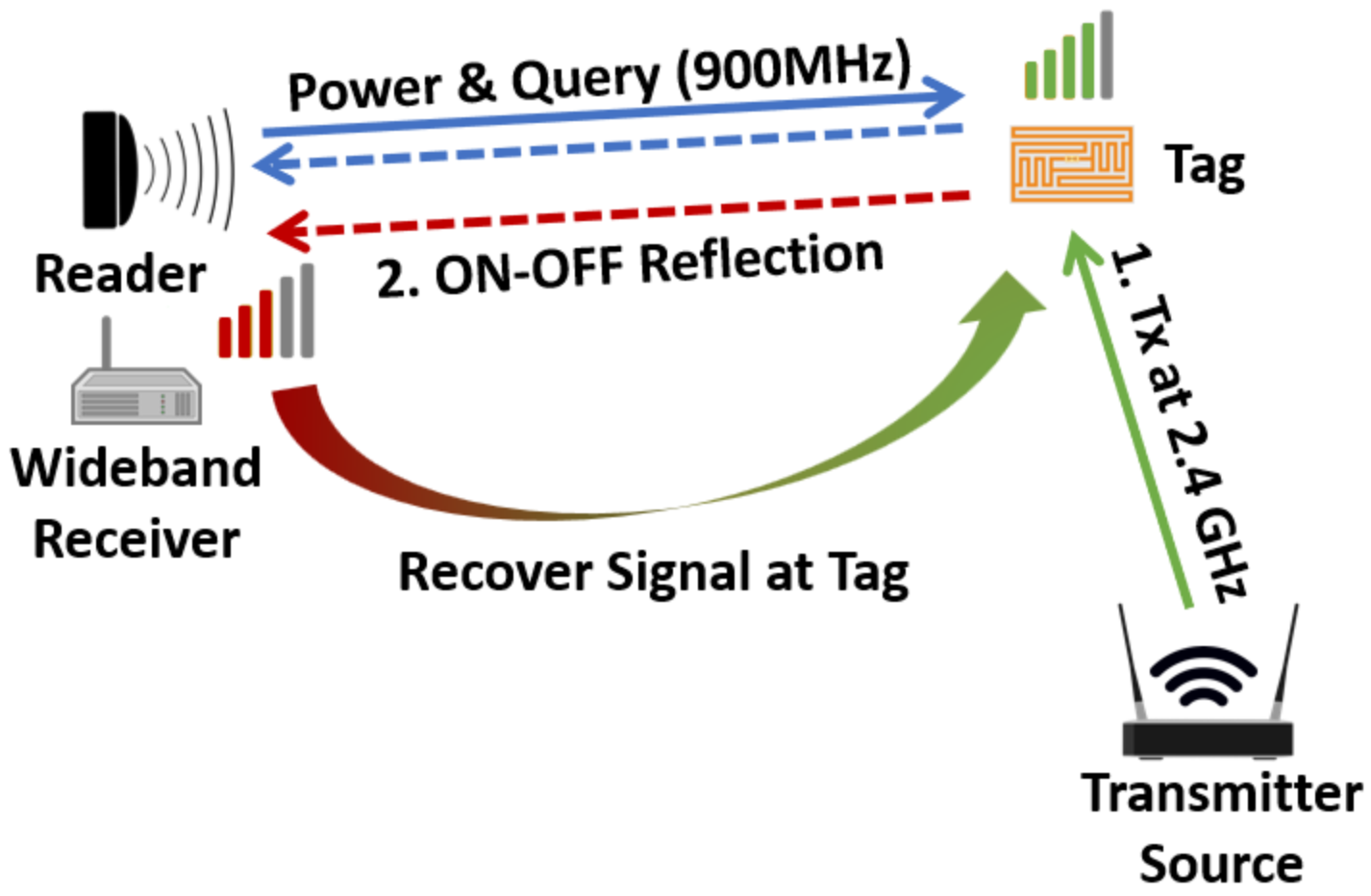
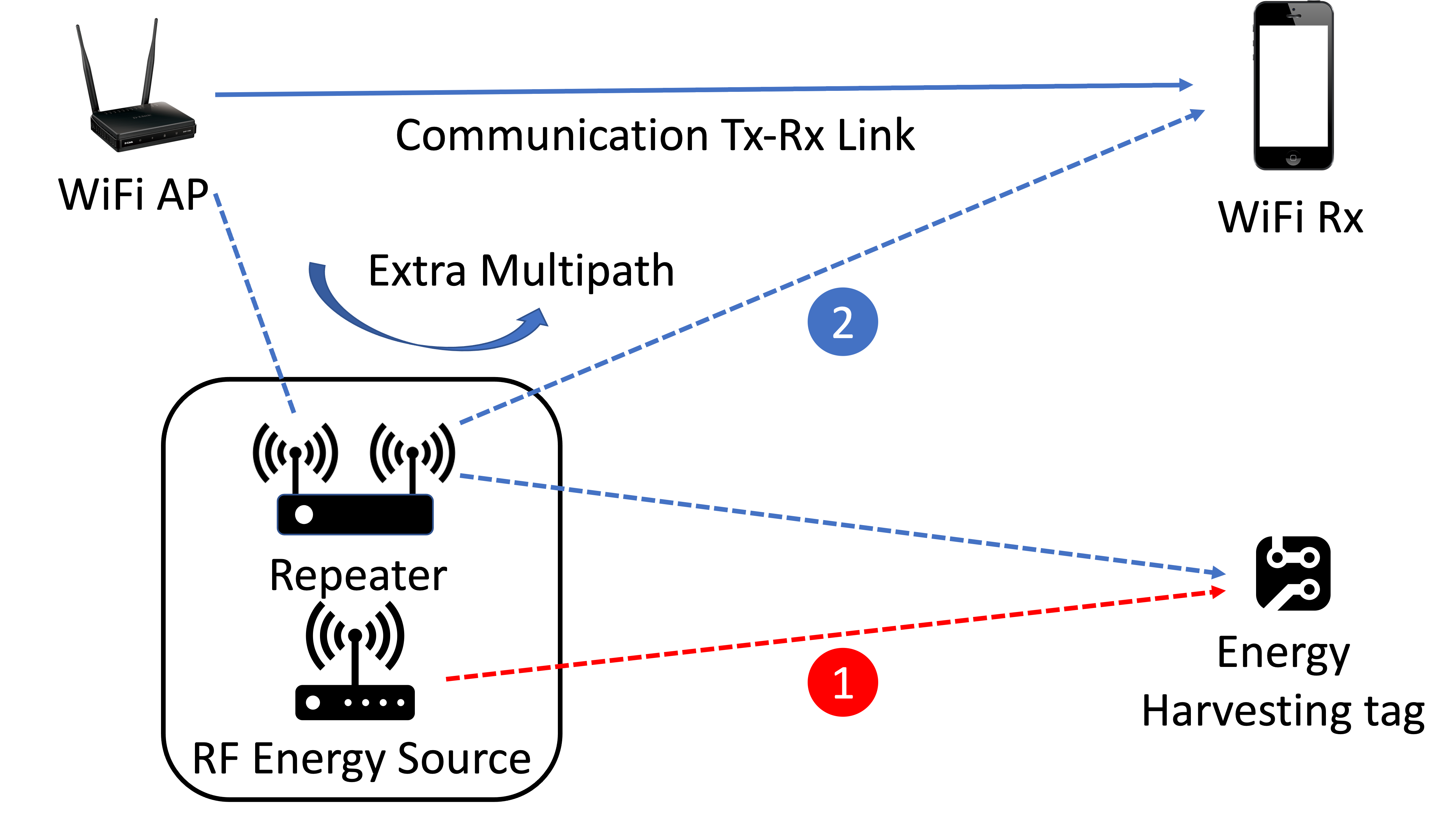
Long Range RF Energy Harvesting
Uninterrupted long range RF energy harvesting can revolutionize current battery-free sensing and networking market. Existing RF energy harvesting is either opportunistic through ambient signals or on demand through dedicated nearby transmitters (readers). This work envisions long range multiband RF energy harvesting using a few multitband readers that supplement ambient energy. We design and implement multiband readers for RF energy harvesting that politely co-exists with traditional communication radios through a combination of careful scheduling of transmissions, carrier sense and signal repeating. Moreover, we propose a frequency selection algorithm to efficiently transfer energy through the most rewarding frequencies.
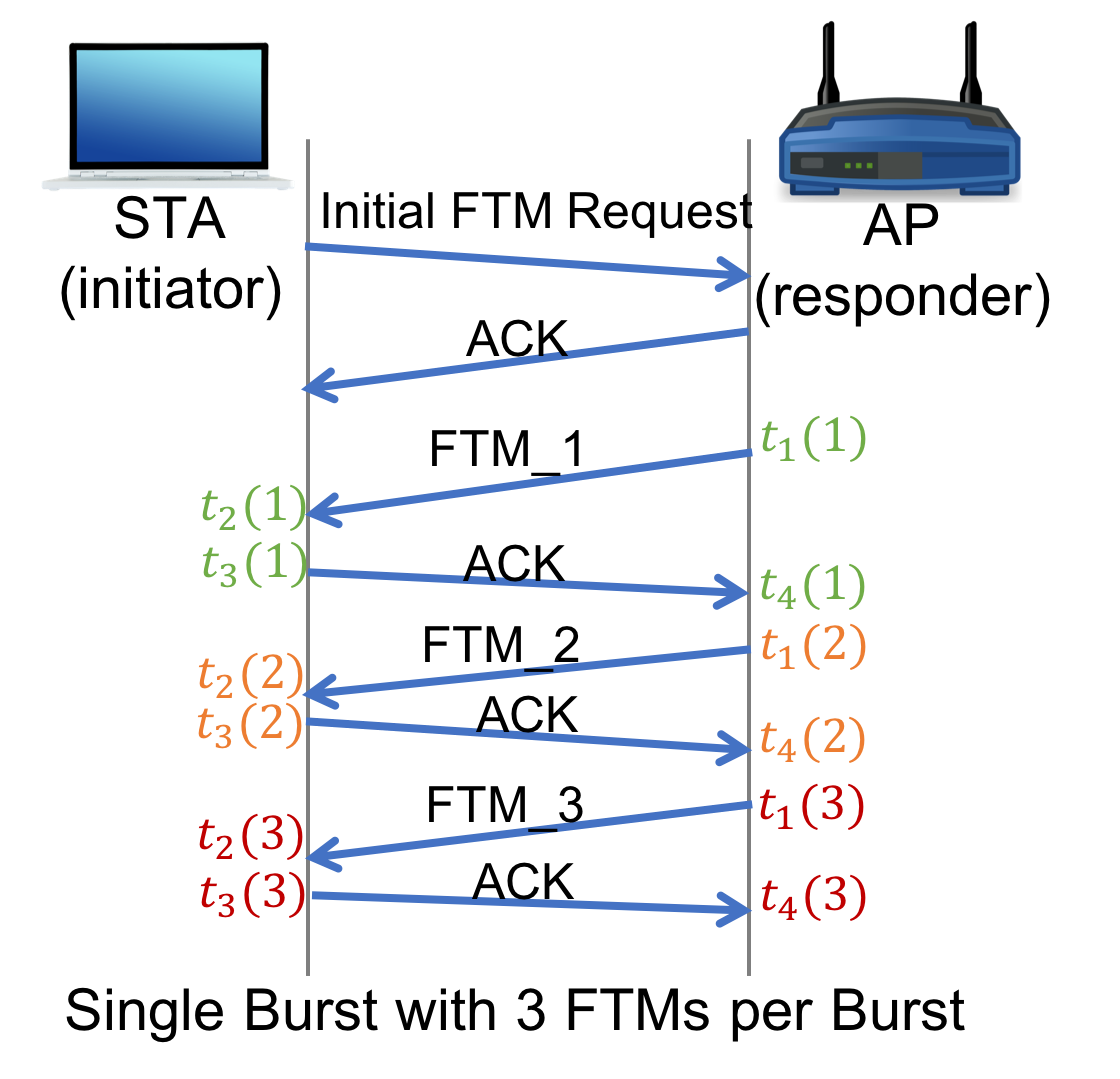
WiFi Fine Time Measurements
Precise indoor positioning, to obtain room-level location or to support indoor navigation has remained stubbornly challenging due to the large effort required to create and maintain WiFi surveys. Similar challenges exist in urban canyons, where GPS accuracy is degraded due to multipath and WiFi positioning cannot entirely replace it. Recently, IEEE 802.11-2016 standardized a FTM protocol that supports such ideas. I introduced for the academic community an open platform for experimenting with FTM as well as a general, repeatable, and accurate measurement framework for evaluating time-based ranging systems. With this open FTM tool, various research applications can be prototyped and experimented for indoor and outdoor sensing. My research shows as well that vehicles can be tracked with meter-level accuracy using WiFi FTMs, an order of magnitude improvement over current mass market vehicle built-in navigation.
Publications
- Vi-Fi: Associating Moving Subjects across Vision and Wireless Sensors Hansi Liu, Abrar Alali, Mohamed Ibrahim, Bryan Bo Cao, Nicholas Meegan, Hongyu Li, Marco Gruteser, Shubham Jain, Kristin Dana, Ashwin Ashok, Bin Cheng, Hongsheng Lu ACM/IEEE IPSN 2022. [PDF] [BibTex]
- Wi-Go: Accurate and Scalable Vehicle Positioning using WiFi Fine Timing Measurement Mohamed Ibrahim, Ali Rostami, Bo Yu, Hansi Liu, Minitha Jawahar, Viet Nguyen, Marco Gruteser, Fan Bai, and Richard Howard ACM MobiSys 2020. [PDF] [BibTex]
- Verification: Accuracy Evaluation of WiFi Fine TimeMeasurements on an Open Platform Mohamed Ibrahim, Hansi Liu, Minitha Jawahar, Viet Nguyen, Marco Gruteser, Richard Howard, Bo Yu, and Fan Bai ACM MobiCom 2018. [PDF] [BibTex]
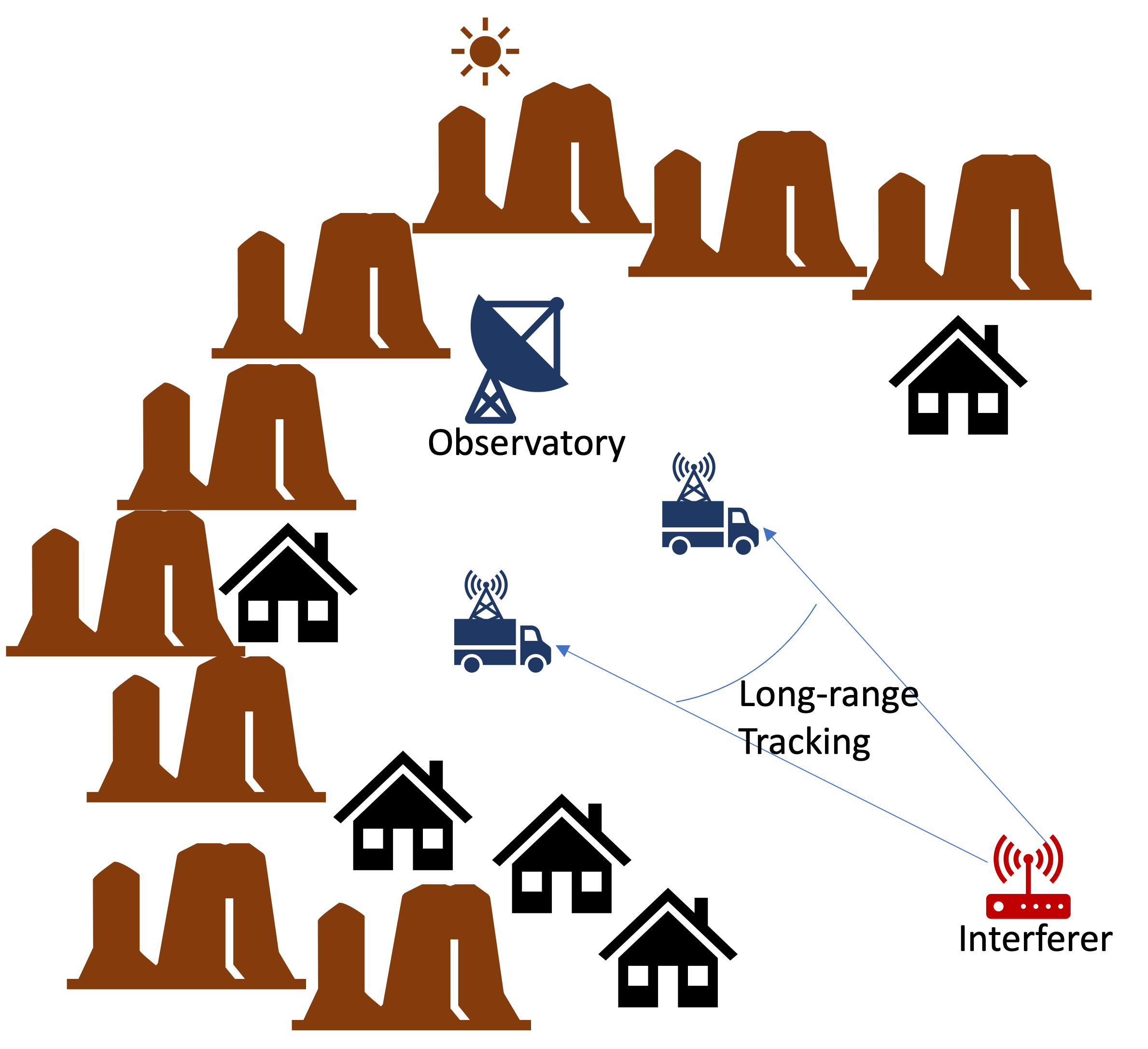
Long Range Interference Detection in Radio Quiet Zones
A clear realization of how wireless networking can benefit from wireless sensing is shown in TranQuil. In which, we address the problem of detecting and localization WiFi AP interfering with Radio astronomy observatories from a kilometer away. However, the range of a WiFi AP is around 100 m, it can still interfere with extremely sensitive radio astronomy towers, which listen to cosmic radiations from space. While radio quiet zones are enforced by law to prohibit transmissions in nearby areas to such observatories, interference still happens due to lack of awareness or accidentally. In this project, we design a long range detection and localization system of WiFi transmitter using an enhanced WiFi beacon packet detection pipeline and time-difference-of-arrival techniques. We evaluate this system in Green Bank observatory, one of the largest radio astronomy observatory in the world, and our system can track WiFi interferer with median error of 13.2 m from about a kilometer away.
Publications
- Long-Range Wi-Fi Localization for Radio Quiet Zones Atul Bansal, Mohamed Ibrahim, Kuang Yuan, Swarun Kumar, and Bob Iannucci Under review, 2022. [PDF] [BibTex]
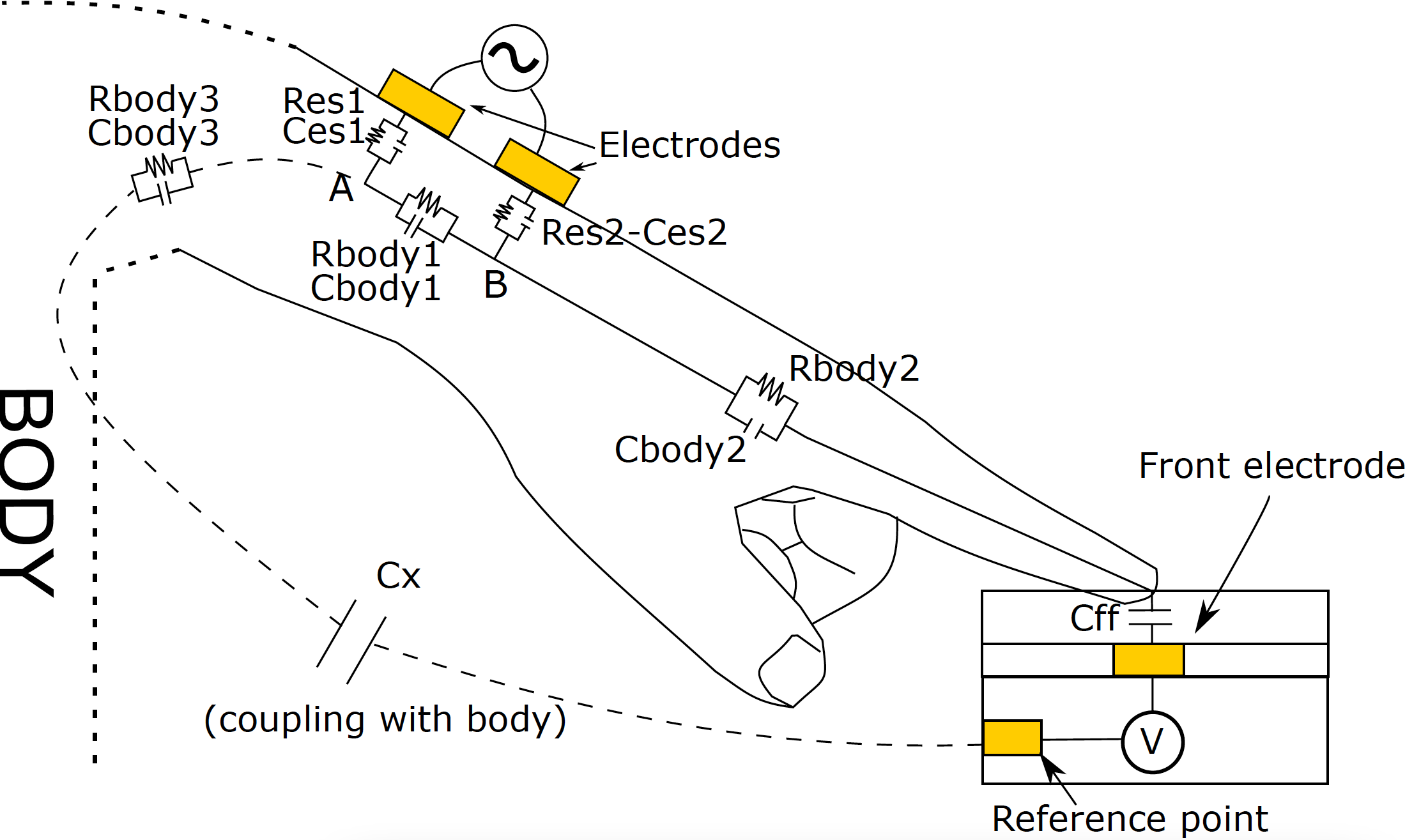
Body-guided Communication
This work studies how wireless signal propagates over human body for secure, low-energy and less interference communication. In this work, we propose on body guided communication using capacitive coupling to secure every touch when users interact with a variety of devices and objects. With this communication system, the transmitted signal only travels through a user’s body and limits the ability to decode the signal off the body. Moreover, this system can construct an energy efficient and secure network of on body devices and support various applications in smart homes and cities. For example, identifying each person in a household through screen touching can personalize the usage of their home amenities and provide convenient and energy efficient access control mechanism.
Publications
- Body-Guided Communications: A Low-power, Highly-Confined Primitive to Track and Secure Every Touch Viet Nguyen, Mohamed Ibrahim, Hoang Truong, Phuc Nguyen, Marco Gruteser, Richard Howard, and Tam Vu IEEE MobiCom 2018. [PDF] [BibTex]
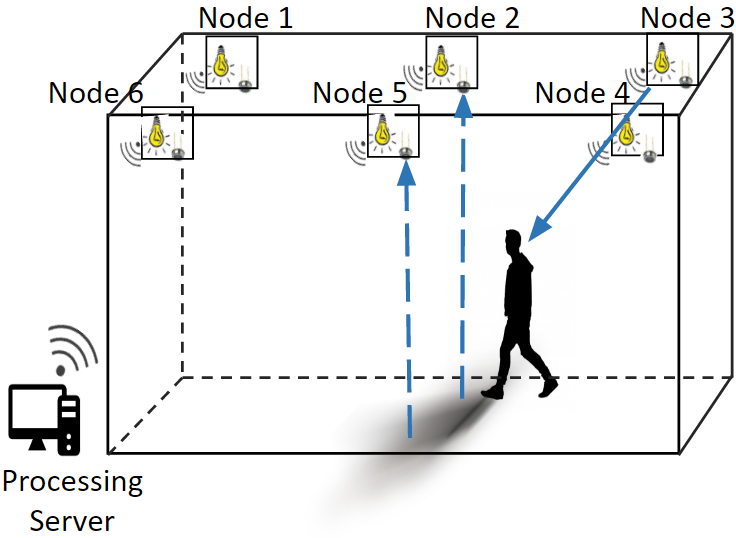
Activity Sensing using Ceiling Photosensors
This paper explores the feasibility of tracking motion and activities of humans using visible light. Shadows created by casting visible light on humans and objects are sensed using sensors that are embedded along with the light sources. Existing Visible Light Sensing (VLS) techniques require either light sensors deployed on the floor or a person carrying a device. Our approach seeks to measure light reflected off the floor to achieve an entirely device-free and light-source based system. We co-locate photosensors with LED light sources to observe the changes in light level occurring on the floor.
Publications
- EyeLight: Light-based Occupancy Estimation and Activity Recognition from Shadows on the Floor Mohamed Ibrahim, Viet Nguyen, Siddharth Rupavatharam, Minitha Jawahar, Marco Gruteser, and Richard Howard IEEE INFOCOM 2018. [PDF] [BibTex]
- Visible Light based Activity Sensing using Ceiling Photosensors Mohamed Ibrahim, Viet Nguyen, Siddharth Rupavatharam, Minitha Jawahar, Marco Gruteser, and Richard Howard ACM VLCS 2016 at MobiCom. Best Paper Award [PDF] [BibTex]
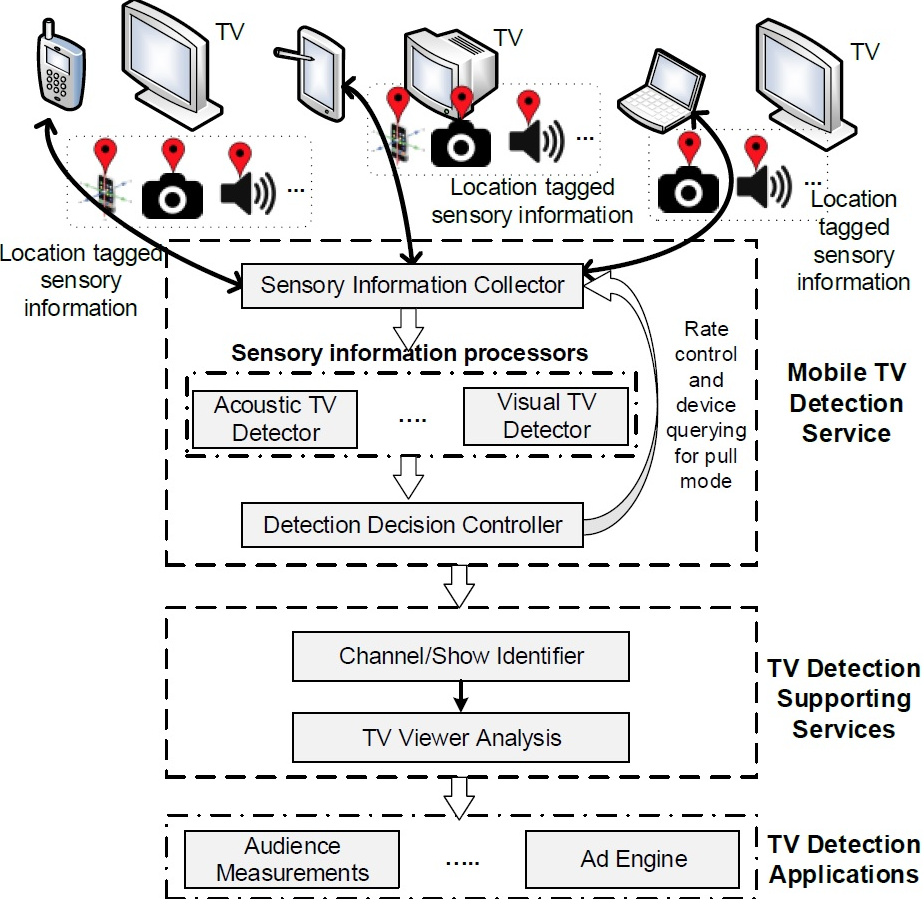
Over-the-air TV Detection using Mobile Phones
This work introduces a mobile sensing technique to detect a nearby active television, the channel it is tuned to, and whether it is receiving this channel over the air. This technique can find applications in tracking TV viewership, second screen services and advertising, as well as improving the efficiency of TV whitespace spectrum usage. The technique uses a three-stage detection process. It first uses a probabilistic model on audio recordings from mobile phones to detect likely TV sounds in the area. It then correlates the recording with known TV channel audio to identify the channel and improve detection robustness. Finally, it applies a latency analysis to determine whether programming is received over-the-air or through alternate means such as cable or satellite TV.
Publications
- Over-The-Air TV Detection using Mobile Devices Mohamed Ibrahim, Marco Gruteser, Khaled A. Harras, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE ICCCN 2017. Invited Paper [PDF] [BibTex]
- Toward dynamic real-time geo-location databases for TV white spaces. Ahmed Saeed, Mohamed Ibrahim, Khaled A. Harras, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE Network, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 76-82, September-October 2015. [PDF] [BibTex]
- Unconventional TV Detection using Mobile Devices Mohamed Ibrahim, Ahmed Saeed, Khaled A. Harras and Moustafa Youssef IARIA UBICOMM 2013- Work-in-progress paper. [PDF] [BibTex]
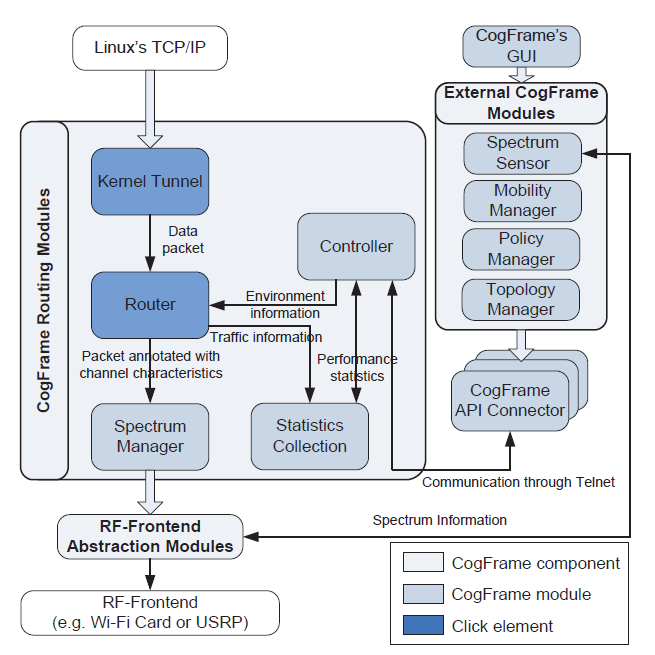
Large-Scale Framework for Cognitive Radio Routing Protocols Testing
Building testbeds for Cognitive Radio Networks (CRNs) is one of the main challenges that can affect the wide deployability of such networks. In this project we develop a framework that facilitates the development of cost-efficient large-scale CRNs routing protocols testbeds. The framework allows the designers to focus on the CRNs routing protocols by abstracting the PHY and MAC layers while providing the necessary cross layer functionalities. CogFrame, our developed framework, allows the development of testbeds that work with standard computers and WiFi cards to reduce the cost while allowing integrating with other special hardware for more flexibility. It also provides different modules for implementing and emulating complex scenarios such as regulatory authority policies, mobility management, topology management.
Publications
- Primary User-aware Optimal Discovery Routing for Cognitive Radio Networks. Arsany Guirguis, Fadel Digham, Karim G Seddik, Mohamed Ibrahim, Khaled A. Harras, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018 [PDF] [BibTex]
- Primary User Aware k-hop Routing for Cognitive Radio Networks Arsany Guirguis, Mohamed Ibrahim, Karim G Seddik, Khaled A. Harras, Fadel Digham, and Moustafa IEEE Globecom 2015. [PDF] [BibTex]
- Routing metrics of cognitive radio networks: A survey. Moustafa Youssef, Mohamed Ibrahim, Mohamed Abdelatif, Lin Chen, and Athanasios V. Vasilakos IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 16.1 (2014): 92-109. [PDF] [BibTex]
- A Low-Cost Large Scale Framework for Cognitive Radio Routing Protocols Testing Ahmed Saeed, Mohamed Ibrahim, Khaled A. Harras and Moustafa Youssef IEEE ICC 2013. [PDF] [BibTex]
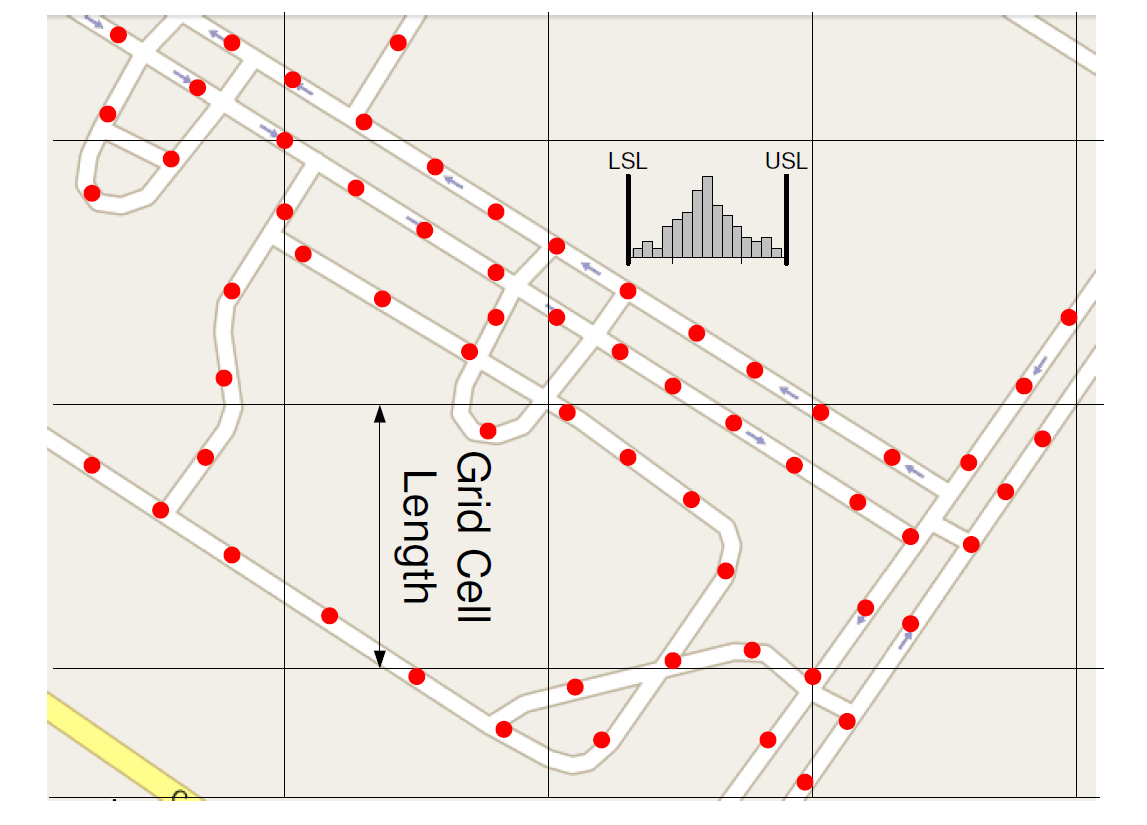
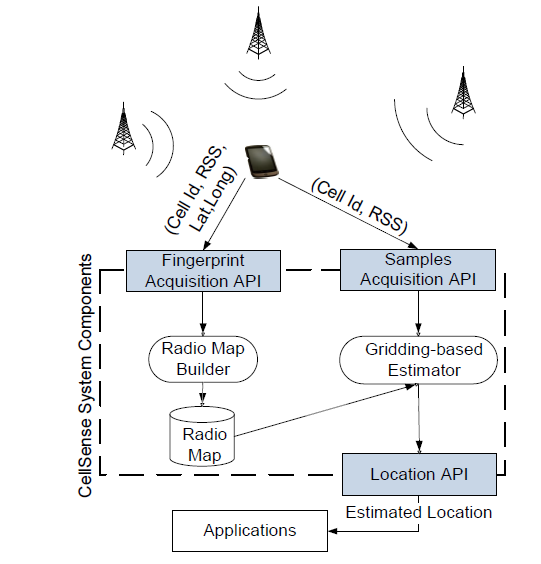
CellSense: An Accurate Energy-Efficient GSM Positioning System
Context-aware applications have been gaining huge interest in the last few years. With cell phones becoming ubiquitous computing devices, cell phone localization has become an important research problem. In this project, we present CellSense, a probabilistic RSSI-based fingerprinting location determination system for GSM phones. We discuss the challenges of implementing a probabilistic fingerprinting localization technique in GSM networks and present the details of the CellSense system and how it addresses these challenges. We then extend the proposed system using a hybrid technique that combines probabilistic and deterministic estimation to achieve both high accuracy and low computational overhead.
Publications
- Enabling Wide Deployment of GSM Localization over Heterogeneous Phones Mohamed Ibrahim, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE ICC 2013. [PDF] [BibTex]
- CellSense: An accurate energy-efficient GSM positioning system. Mohamed Ibrahim, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 61.1 (2012): 286-296. [PDF] [BibTex]
- A Hidden Markov Model for Localization Using Low-End GSM Cell Phones Mohamed Ibrahim, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE ICC 2011. [PDF] [BibTex]
- CellSense: A Probabilistic RSSI-based GSM Positioning System Mohamed Ibrahim, and Moustafa Youssef IEEE Globecom 2010. [PDF] [BibTex]